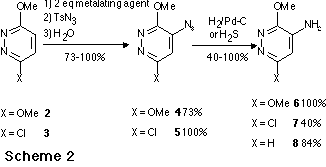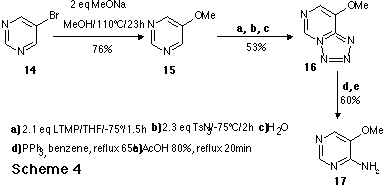A new route to aminodiazines
via metalation reaction. Synthesis of an aza analogue of nevirapine
Karine Couture, Nelly Plé, Alain Turck, Guy Quéguiner
Laboratoire de Chimie Organique Fine de l'IRCOF associé au CNRS, INSA de Rouen, BP 08, F-76131 Mont-Saint-Aignan cédex, France
Fax + 33(35)528484
Several antibacterial sulfonamides such as Sulfadiazine, Madribon,
Sulfamethoxypyridazine, CS 61, Kelfizine are usually manufactured by reaction
of acetamidobenzenesulfonyl chloride with the aminoderivative of a diazine. The
aminomethoxydiazines are generally the precursors of these
sulfonamides.
A new route to aminodiazines is reported, the ortho-directed
lithiation of diazines is used, followed by reaction with tosylazide as an
electrophile. The reduction of the azido or tetrazolo compounds obtained was
achieved and led to the expected amines. This methodology has allowed to
synthesis of new aminodiazines and an improvement in the yield of
various aminodiazines previously described.
As an application to the new route to aminodiazines, we report the synthesis of
an aza analogue 2 of the Nevirapine 1 , a highly selective
non-competitive inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase.
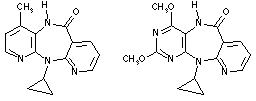
Nevirapine 1 2
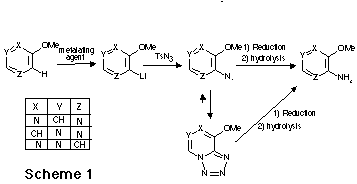
The general principle of this new synthetic route to aminomethoxydiazines via
metalation is summarized the Scheme 1. Treatment of a methoxydiazine with a
twofold excess of metalating agent in THF at - 75 oC followed by reaction
with tosylazide led to the expected azido derivative. However when the azido
group was ortho to a ring nitrogen atom, a fast cyclisation occurred leading to
a tetrazolo derivative. A further reduction applied to the azido or tetrazolo
derivative led to the expected aminodiazine
Aminopyridazines
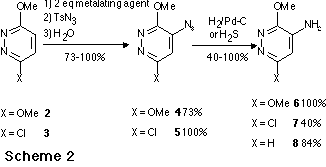
Aminopyrazine
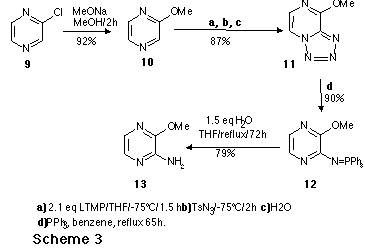
Aminopyrimidine
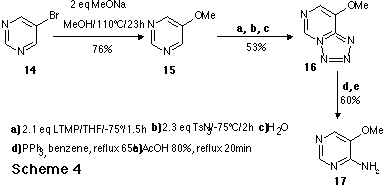
As an application to the new route to aminodiazines, we report here the
synthesis of an aza analogue of the Nevirapine 1. Nevirapine is a highly
selective, non-competitive inhibitor of HIV-1 reverse transcriptase which is
currently undergoing phase II clinical evaluation for the treatment of
HIV-infected individuals. The synthesic sequence of the aza analogue 2
is outlined in Scheme 5.
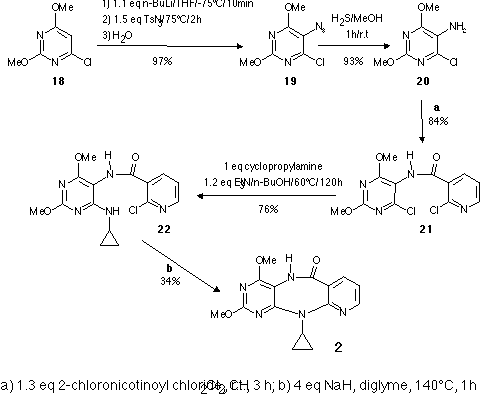
Scheme 5